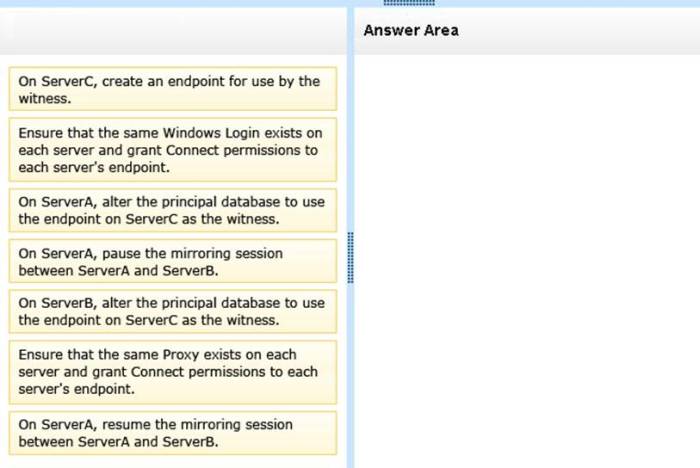
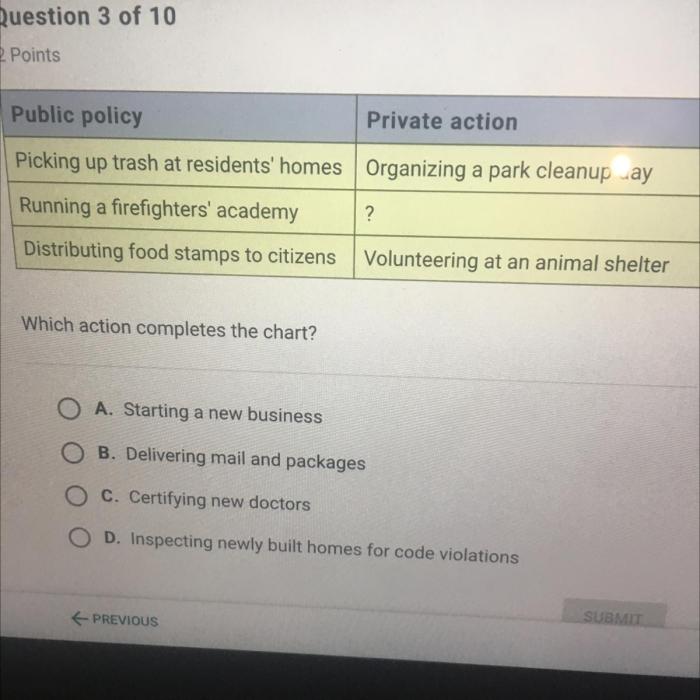
Which action completes the chart – Determining the appropriate action to complete a chart is crucial for accurate data interpretation and decision-making. This comprehensive guide explores the significance of understanding completion actions, analyzes various chart types and their corresponding actions, and delves into the methods and applications of chart completion.
Identifying Completion Actions: Which Action Completes The Chart
Understanding which action completes a chart is crucial for accurate data interpretation. It ensures that the missing information is filled in a way that aligns with the chart’s purpose and data relationships.
Examples of charts with missing completion actions include: a line chart with a missing data point, a bar chart with an incomplete bar, or a pie chart with a missing slice.
Analyzing Chart Types, Which action completes the chart
Different chart types have specific completion actions that are appropriate for their respective data structures.
| Chart Type | Completion Action |
|---|---|
| Line Chart | Interpolation or Extrapolation |
| Bar Chart | Data Replacement |
| Pie Chart | Data Allocation |
Factors that influence the choice of completion action include the data distribution, the desired level of accuracy, and the purpose of the chart.
Exploring Data Relationships
The data relationships within a chart determine the most appropriate completion action.
For example, if the data points in a line chart follow a linear trend, interpolation or extrapolation can be used to fill in the missing point. If the data in a bar chart represents discrete categories, data replacement is the most suitable action.
Methods for Completing Charts
Various methods can be used to complete charts, including:
- Interpolation: Estimating the value of a missing data point based on the surrounding data points.
- Extrapolation: Predicting the value of a data point beyond the range of the existing data.
- Forecasting: Predicting future values based on historical data.
Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice depends on the specific chart and data.
Practical Applications
Completing charts is a valuable skill in various fields.
For example, in finance, completing charts can help identify trends and predict market movements. In healthcare, completing charts can assist in diagnosing diseases and monitoring patient progress.
By filling in missing data, charts provide a more complete and accurate representation of the underlying information, leading to enhanced decision-making and problem-solving.
Quick FAQs
What factors influence the choice of completion action?
Factors include the chart type, data distribution, and the desired level of accuracy.
What are the advantages of using interpolation for chart completion?
Interpolation provides a smooth transition between known data points, making it suitable for continuous data.
How can chart completion enhance decision-making?
By completing charts, users can identify trends, patterns, and outliers, which can inform decision-making and problem-solving.