Membrane function POGIL answers PDF provides a detailed examination of the fundamental principles governing biological membranes. This guide delves into the intricate structure, diverse components, and critical roles of membranes in cellular processes, offering a comprehensive understanding of their significance in maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating intercellular communication.
The document explores the basic architecture of membranes, highlighting the interplay between lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. It elucidates the mechanisms of membrane transport, encompassing passive and active transport, and emphasizes the importance of membrane channels and pumps in maintaining cellular gradients.
Additionally, the guide delves into the concept of membrane potential, its contributing factors, and its implications for cell signaling.
Membrane Structure and Function
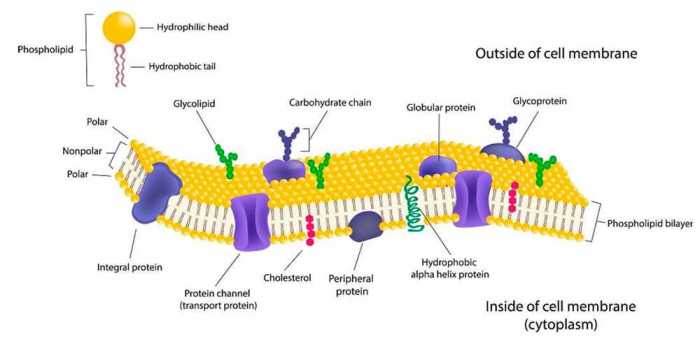
Biological membranes are thin, flexible barriers that enclose cells and their organelles. They regulate the passage of materials into and out of the cell, and they play a crucial role in cell signaling and communication.
The basic structure of a biological membrane is a lipid bilayer. The lipid bilayer is composed of two layers of phospholipids, which are amphipathic molecules with a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail. The hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids face each other in the center of the membrane, while the hydrophilic heads face outward, interacting with the aqueous environment on either side of the membrane.
Membrane Lipids
- Phospholipids are the most abundant type of lipid in biological membranes.
- Other types of lipids found in membranes include cholesterol, glycolipids, and sphingolipids.
- Cholesterol helps to maintain the fluidity of the membrane and prevents it from becoming too rigid.
- Glycolipids and sphingolipids are involved in cell signaling and recognition.
Membrane Proteins
- Membrane proteins are embedded in the lipid bilayer and span the entire membrane.
- They play a variety of roles, including transporting molecules across the membrane, signaling between cells, and anchoring the membrane to the cytoskeleton.
- There are two main types of membrane proteins: integral proteins and peripheral proteins.
- Integral proteins are embedded in the lipid bilayer, while peripheral proteins are attached to the surface of the membrane.
Membrane Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates are attached to the extracellular surface of the membrane in the form of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
- They play a role in cell recognition and adhesion.
- Glycoproteins are involved in cell signaling and communication.
Membrane Transport
Membrane transport is the movement of molecules across the cell membrane. There are two main types of membrane transport: passive transport and active transport.
Passive Transport
- Passive transport is the movement of molecules across the membrane without the expenditure of energy.
- It occurs when there is a concentration gradient across the membrane.
- There are three types of passive transport: simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis.
- Simple diffusion is the movement of molecules across the membrane down their concentration gradient.
- Facilitated diffusion is the movement of molecules across the membrane with the help of a membrane protein.
- Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration.
Active Transport
- Active transport is the movement of molecules across the membrane against their concentration gradient.
- It requires the expenditure of energy in the form of ATP.
- There are two types of active transport: primary active transport and secondary active transport.
- Primary active transport is the movement of molecules across the membrane using an ATP-powered pump.
- Secondary active transport is the movement of molecules across the membrane using the energy stored in an electrochemical gradient.
Membrane Channels and Pumps
- Membrane channels are proteins that form pores in the membrane.
- They allow molecules to pass through the membrane without the expenditure of energy.
- Membrane pumps are proteins that use ATP to transport molecules across the membrane against their concentration gradient.
Membrane Potential: Membrane Function Pogil Answers Pdf
Membrane potential is the difference in electrical charge across the cell membrane.
It is caused by the unequal distribution of ions across the membrane.
The membrane potential is important for cell signaling and communication.
Factors that Contribute to Membrane Potential
- The concentration gradient of ions across the membrane.
- The permeability of the membrane to different ions.
- The activity of ion pumps and channels in the membrane.
Role of Membrane Potential in Cell Signaling
- Membrane potential is used to transmit signals between cells.
- When a cell receives a signal, it can change its membrane potential.
- This change in membrane potential can then trigger a cascade of events that lead to a cellular response.
Membrane Fluidity
Membrane fluidity is the ability of the membrane to move and flow.
It is important for cell function because it allows the membrane to adapt to changes in the environment.
The fluidity of the membrane is determined by the composition of the membrane lipids.
Factors that Affect Membrane Fluidity, Membrane function pogil answers pdf
- The length of the fatty acid chains in the phospholipids.
- The degree of unsaturation of the fatty acid chains.
- The presence of cholesterol in the membrane.
Role of Membrane Fluidity in Cell Function
- Membrane fluidity is important for cell signaling and communication.
- It also plays a role in cell growth and division.
- Membrane fluidity is essential for the proper function of membrane proteins.
Membrane Signaling
Membrane signaling is the process by which cells communicate with each other.
It involves the binding of a signaling molecule to a receptor on the cell membrane.
The binding of the signaling molecule to the receptor triggers a cascade of events that lead to a cellular response.
Types of Membrane Receptors
- There are two main types of membrane receptors: G protein-coupled receptors and ion channel receptors.
- G protein-coupled receptors are linked to a G protein, which is a protein that activates other proteins inside the cell.
- Ion channel receptors are directly linked to an ion channel, which allows ions to flow across the membrane.
Mechanisms of Signal Transduction Across Membranes
- There are two main mechanisms of signal transduction across membranes: second messengers and protein kinases.
- Second messengers are small molecules that are produced inside the cell in response to the binding of a signaling molecule to a receptor.
- Protein kinases are enzymes that phosphorylate other proteins, which can activate or deactivate them.
Role of Membrane Signaling in Cell Communication
- Membrane signaling is essential for cell communication.
- It allows cells to send and receive signals from each other.
- Membrane signaling plays a role in a variety of cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and metabolism.
Top FAQs
What is the primary function of biological membranes?
Biological membranes serve as barriers that separate different compartments within cells and regulate the movement of substances across these compartments.
How do membrane proteins contribute to membrane function?
Membrane proteins facilitate the transport of molecules across membranes, participate in signal transduction, and provide structural support to the membrane.
What is the role of membrane fluidity in cellular function?
Membrane fluidity allows membranes to adapt to changes in their environment and facilitates the movement of membrane components, which is essential for various cellular processes.