Under the new deal federalism is frequently described as – Under the New Deal, federalism in the United States underwent a profound transformation, characterized by a shift towards cooperative, fiscal, regulatory, and intergovernmental dimensions. This essay delves into the complexities of this reimagined federalism, examining its historical context, key principles, and lasting impact.
The New Deal era witnessed an unprecedented expansion of federal power, as the federal government assumed a more active role in addressing the economic and social challenges of the Great Depression. This shift marked a departure from the traditional understanding of federalism, which emphasized state autonomy and limited federal intervention.
Cooperative Federalism
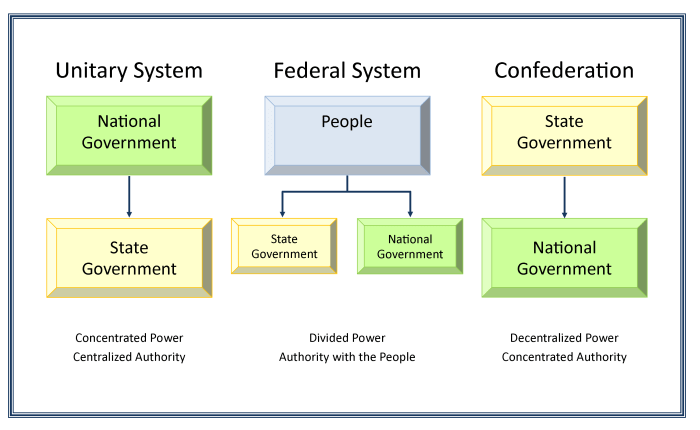
Cooperative federalism emerged in the early 20th century as a response to the growing complexity of American society. It recognized the need for both federal and state governments to work together to address national problems. The New Deal expanded cooperative federalism by increasing federal involvement in areas traditionally reserved for states, such as welfare and economic regulation.
Shared Responsibilities
Cooperative federalism emphasized the shared responsibilities between federal and state governments. The federal government provided financial assistance and policy guidance, while states retained significant autonomy in implementing programs. This arrangement allowed the federal government to address national priorities while respecting state sovereignty.
Fiscal Federalism

Fiscal federalism refers to the financial relationships between federal, state, and local governments. The New Deal significantly expanded fiscal federalism by providing grants-in-aid and loans to states and localities. These funds supported a wide range of programs, including unemployment relief, infrastructure projects, and social welfare.
Impact on Federal Power
Fiscal federalism played a crucial role in expanding federal power. By providing financial assistance, the federal government gained influence over state and local policies. States became increasingly reliant on federal funding, which gave the federal government leverage in shaping state decisions.
Regulatory Federalism
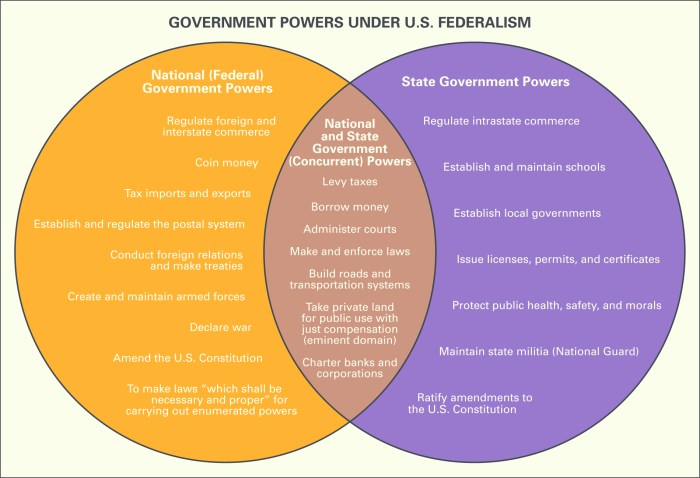
Regulatory federalism refers to the use of federal regulations to shape state and local policies. The New Deal expanded federal regulatory power through agencies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission and the Federal Communications Commission. These regulations established national standards and guidelines, which states had to comply with.
Balance between Federal Authority and State Autonomy, Under the new deal federalism is frequently described as
Regulatory federalism raised concerns about the balance between federal authority and state autonomy. States argued that federal regulations infringed on their rights to self-governance. However, the federal government maintained that regulations were necessary to protect national interests and ensure uniformity.
Intergovernmental Relations

The New Deal transformed intergovernmental relations. The federal government created new agencies, such as the Federal Emergency Relief Administration, to coordinate with states and localities. Federal-state commissions and conferences were established to facilitate communication and cooperation.
Impact on State and Local Governments
The expansion of federal agencies had a significant impact on state and local governments. Federal agencies provided funding, technical assistance, and policy guidance. This increased federal influence over state and local affairs, but also provided states with resources to address pressing problems.
Essential FAQs: Under The New Deal Federalism Is Frequently Described As
What were the key principles of cooperative federalism under the New Deal?
Cooperative federalism emphasized shared responsibilities between the federal and state governments, with the federal government providing financial and technical assistance to support state and local programs.
How did fiscal federalism contribute to the expansion of federal power?
Fiscal federalism involved the use of federal grants and loans to support state and local programs, giving the federal government greater influence over policymaking and program implementation.
What was the impact of regulatory federalism on state and local policies?
Regulatory federalism allowed the federal government to establish minimum standards and regulations that states and localities had to comply with, limiting their autonomy in certain policy areas.