Exercise 30 review sheet anatomy of the heart – Embarking on an exploration of the heart’s intricate anatomy, Exercise 30 Review Sheet: Anatomy of the Heart Unveiled, delves into the depths of this vital organ, unraveling its structure, function, and clinical significance.
From its external features to its internal chambers, valves, and blood flow patterns, this comprehensive review sheet provides a thorough understanding of the heart’s anatomy and its role in maintaining cardiovascular health.
Definition and Function of the Heart: Exercise 30 Review Sheet Anatomy Of The Heart
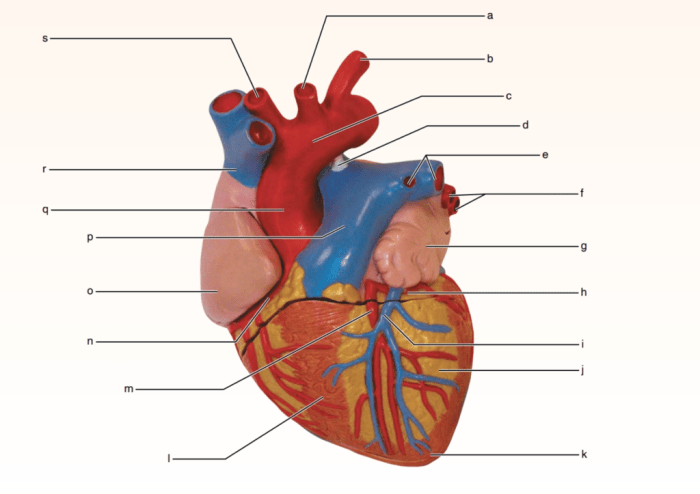
The heart is a muscular organ located in the thoracic cavity, medially between the lungs. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, providing oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products.The heart is divided into two sides: the right side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, while the left side pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
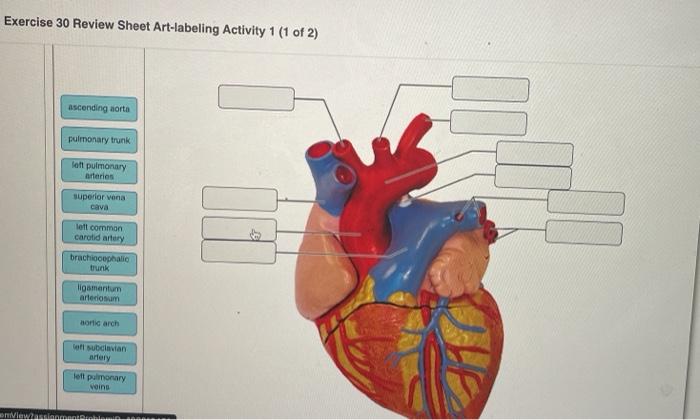
External Anatomy of the Heart
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Pericardium | Fibrous sac that surrounds and protects the heart |
| Apex | Pointed lower tip of the heart |
| Base | Broader upper portion of the heart |
| Chambers | Atria (upper chambers) and ventricles (lower chambers) |
| Valves | Tricuspid valve (between right atrium and ventricle), pulmonary valve (between right ventricle and pulmonary artery), mitral valve (between left atrium and ventricle), aortic valve (between left ventricle and aorta) |
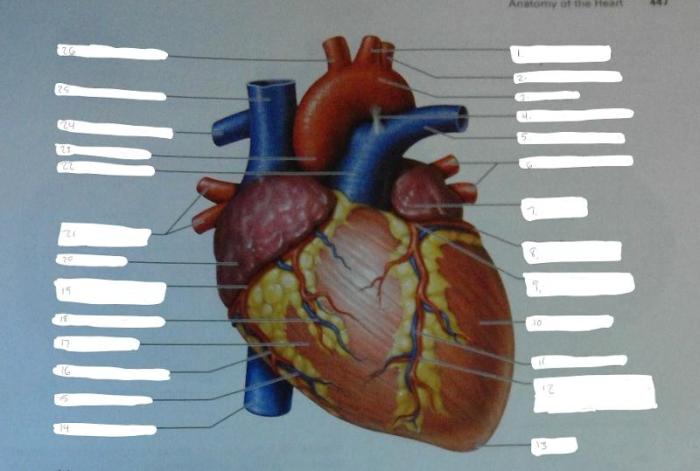
Internal Anatomy of the Heart
Chambers:
Atria
Thin-walled chambers that receive blood from the body (right atrium) or lungs (left atrium)
Ventricles
Thick-walled chambers that pump blood to the lungs (right ventricle) or body (left ventricle)Septa:
Atrial septum
Wall separating the right and left atria
Ventricular septum
Wall separating the right and left ventriclesPapillary Muscles and Chordae Tendineae:
Papillary muscles
Projections from the ventricular walls
Chordae tendineae
Tendons that connect papillary muscles to the valves, preventing them from everting during ventricular contractionCoronary Arteries and Veins:
Coronary arteries
Supply blood to the heart muscle
Coronary veins
Drain blood from the heart muscle
Blood Flow Through the Heart, Exercise 30 review sheet anatomy of the heart
Pulmonary Circulation:
- Deoxygenated blood from the body enters the right atrium
- Blood flows through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle
- Right ventricle pumps blood through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary artery carries blood to the lungs for oxygenation
Systemic Circulation:
- Oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left atrium
- Blood flows through the mitral valve into the left ventricle
- Left ventricle pumps blood through the aortic valve into the aorta
- Aorta distributes oxygenated blood to the body
Coronary Circulation:
- Blood from the aorta enters the coronary arteries
- Coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscle
- Blood from the heart muscle drains into the coronary veins
- Coronary veins return blood to the right atrium
Common Queries
What is the primary function of the heart?
The heart’s primary function is to pump oxygenated blood throughout the body and remove deoxygenated blood from the body.
What are the four chambers of the heart?
The four chambers of the heart are the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
What is the purpose of the valves in the heart?
The valves in the heart prevent backflow of blood and ensure proper blood flow through the heart’s chambers.